In the ever-evolving world of technology, it seems like there's always a new buzzword or concept to wrap our heads around. From natural language processing to generative AI, it's easy to get lost in the jargon.
Whether you're an AI enthusiast or a curious learner, this glossary will provide you with the essential understanding of key terms and concepts needed to navigate the intelligent virtual assistant (IVA) landscape effortlessly.
So sit back, relax, and get ready to explore the exciting world of IVA technology!
Key Terms for Building Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence, often referred to as AI, is a remarkable field of technology that focuses on creating computer systems capable of imitating human-like intelligence. These advanced systems are designed to carry out tasks that traditionally require human abilities, such as making decisions, recognizing and understanding speech, translating between different languages, and so much more.
API
An API, also known as an Application Programming Interface, is a powerful tool that assists developers in constructing software applications. It consists of a collection of definitions, protocols, and tools that serve as the fundamental building blocks for creating programs.
Auto-NLP
A term we use to describe our synonym-based approach to natural language processing. It allows IVAs to communicate and understand intent variations right out of the gate, thus being speech-enabled “automatically”
Automatic Message Formatting
The pre-programmed responses for tasks built into the Kore.ai XO Platform Natural Language (NL) engines.
Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) – Our Platform can integrate an Automated Speech Recognition Engine to enable bots to process voice-driven interactions and communicate outside of traditional text-based interfaces.
Kore.ai Bot Builder Tool
The Kore.ai XO Platform offers a user-friendly web-based Bot Builder that empowers enterprises to tailor their Intelligent Virtual Assistant (IVA) use cases, channels, tasks, security measures, and much more. With this innovative tool, developers can easily design, test, and deploy Virtual Assistants (VAs) in a streamlined and efficient manner. This cohesive framework ensures consistency and scalability for businesses of all sizes.
Bot Context – User or task information that is captured at the bot level and can be used in context with some or all of the users of that bot.
Channel
A channel is another word for any of the various communication platforms where an IVA can be implemented such as SMS, email, mobile apps, websites, messaging apps, and more. With the Kore.ai XO Platform, you can design IVA tasks once and then deploy them across channels simply by checking a box. You can also differentiate cross-channel experiences by altering message responses or leveraging channel-specific UI elements, such as date selectors, carousels, and more.
Cloud (or Cloud computing)
Internet-based computing that provides shared computer processing resources and data to computers and other devices, on demand.
Cloud Connector
Provides an agent that runs behind your enterprise firewall and acts as a bridge to facilitate secure data exchanges between on-prem systems and the Kore.ai cloud-based infrastructure.
Component Reusability
The ability for developers to use components they’ve already built in the Bot Builder, such as APIs, synonyms, tasks, etc., and apply them to other bots.
Context (see also, Bot Context, Enterprise Context, Session Context, User Context)
The information that an IVA pulls from a conversation with a user that can be leveraged when performing tasks. Contextual data can vary in importance, utility, and lifespan.
Conversational UI
Another way of describing text and voice-based interfaces, which don’t require graphical elements for use, such as Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri.
Cognitive Services (aka Conversational and Cognitive Services)
A collection of separate APIs, SDKs, and services (that run on a cloud infrastructure like Azure) that developers can use to build intelligence into apps and/or to construct an IVA that can leverage AI capabilities.
Data retention
The continued storage of an organization’s data for compliance or business matters.
Deep learning
An area of Machine Learning that is based on learning data representations as opposed to task-specific algorithms.
Deployment
The process of publishing an intelligent virtual assistant to a communication channel where it will be engaged by users.
Dialog task
Dialog tasks are advanced tasks that developers design with logic-driven business processes and pre-established workflows. Bots key off the primary request intent to accomplish the task at hand, then go above and beyond to execute sub-intents and additional workflows. This way, IVAs can handle complex multi-turn conversational experiences that replicate the natural back-and-forth exchanges people have every day.
Dialog Builder – The Dialog Builder gives designers and developers the flexibility to manipulate the entire dialog process of a bot interaction and string together complex workflows in a GUI-based tool.
E-discovery – Any process in which electronic data is sought, located, secured, and searched with the intent of legal use. The Kore.ai XO Platform supports e-discovery.
End-to-End – A way of describing the Kore.ai XO Platform which signifies that it includes all the component features to take enterprises from the very beginning of the IVA development process all the way through deployment and management.
Enterprise Analytics – The central dashboard within the Kore.ai XO Platform where administrators can get visibility into key metrics, pull detailed reports, and track bot usage (i.e. number of executed tasks, most popular channels, most active users, user enrollment, etc.)
Enterprise Bots Store – A bot store that an enterprise sets up for a select group of users to access any custom-built bots. The Store is where you can find prebuilt bot templates that you can use for different business scenarios.
Enterprise-Grade – A way of describing all of the components and capabilities of the Kore.ai XO Platform that are specifically designed to match the highest enterprise standards, including administration, analytics, security, compliance, and more.
Enterprise Context – Information that represents company-wide rules and standards that apply to all users and IVAs, such as a company travel policy, or expense limits.
Entity – Entities are the necessary fields, data, or words for an IVA to complete the user’s request: be that a date, a time, a location, a description, or any number of things. With the required entities in hand, the IVA can reach out to the web service and get the specific data or perform the action as per the user intent.
For example, to book a flight, the IVA needs the source and destination city along with the travel date. In this example, the user utterance “Book me a flight to Orlando for next Sunday”, “Orlando” and “next Sunday” are entities.
Entity Extraction
This is the process by which the Natural Language (NL) engine identifies words from a user’s utterance to ensure all available fields match the task at hand. If the IVA needs an entity to complete the task after initial extraction, it will prompt the user for it.
FAQ
One of the primary data sources an IVA uses, along with the Knowledge Graph, to pull information to complete knowledge tasks.
Framework
A framework is a structure that provides some basic building blocks and generic functionality for building IVAs (like ML/ NLP or a Dialog Builder), but requires additional user-written code or other third-party services (to match the functionality of an actual platform). Frameworks often are composed of piecemeal components from different vendors.
Fundamental Meaning
Fundamental Meaning (FM) is an approach to NLP that’s all about understanding words themselves. Each user utterance is broken down word-for-word to search for intent (what the user is asking the VA to do) and entities (the necessary data needed to complete a task). Learn more about this approach and the Natural Language (NL) engine.
Graphic User Interface (GUI)
A visual way of interacting with an app or system, usually consisting of buttons, images, windows, icons, menu forms, and more.
Information Task
Information tasks look up data or pull reports based on specific parameters and quickly return easy-to-consume results that are convenient for users. These reports are formatted and organized based on user preferences and applicable filters, that can be downloaded for later use. For example, an IVA can provide a sales manager with a report detailing the top 10 sales reps last year by region, organized from most to least sales.
Interface
A shared boundary across which two or more separate components of a computer system exchange information.
Intelligence (see also Platform Intelligence)
All the capabilities provided to developers who use the Kore.ai XO Platform to create AI-powered intelligent virtual assistants including how to use contextual data, memory, NLP, machine learning (both supervised and unsupervised), sentiment analysis, and more.
Intent
A few essential words in an utterance that describe what the user wants the IVA to do. It is usually a combination of a verb and a noun. For example, in “Book me a flight to Orlando for next Sunday”, the intent is Book me a flight.
Intent recognition
The process by which the Natural Language (NL) engine analyzes the structure of a user’s command to identify each word by meaning, position, conjugation, capitalization, plurality, and other factors to correctly match the user’s intent to the task at hand.
Knowledge Task / Knowledge Graph
Knowledge tasks take user questions and search a predefined set of information to rapidly find the right answers, such as hours of operation or specific policy questions.
Live Agent Handoff
An IVAs ability to seamlessly take a conversation from any channel and send it to a human agent. This function is especially useful for customer service, employee support, and ITSM.
Location Services
Location services identify a user’s physical location and can be used to build location-dependent tasks for greater accuracy.
Logic programming
A type of programming that is largely based on formal logic and is the building block for complex IVA dialogs and workflows.
Machine Learning
Using algorithms, patterns, and training data, machine learning allows computers to find hidden insights without having to be explicitly programmed. Learn more about the way that Kore.ai uses machine learning for natural language enablement.
Memory
Intelligent virtual assistants can remember actions, data, and contextual details to maintain conversational continuity and take helpful actions. The bot developer can designate how long the bot remembers information as either short-term or long-term memory.
Message Broker
A Kore.ai XO Platform component that consumes all user inputs and system outputs and standardizes them for a common messaging paradigm that redirects to the appropriate endpoints.
Message Store
A Kore.ai XO Platform component that stores messages between users, bots, and systems and automatically logs and categorizes message successes and failures.
Middleware
The Kore.ai XO Platform Middleware contains the Message Broker, Message Store, and built-in encryption to create a flawless conversational experience by ensuring messages are received, secured, and exchanged in real-time.
Mobile SDKs
A set of software development tools that allow developers to create applications for a variety of mobile devices. Mobile SDKs are also a supported channel for bots.
Multi-Layer Authentication
A method of access control in which the user must provide several separate authentication factors before being granted access to data. The Kore.ai XO Platform supports multi-layer authentication for bot access.
Natural Language (NL)
The method by which users can talk to systems in everyday language like text and speech, rather than programming language.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
The process by which an IVA or any other system understands and processes requests in natural language, rather than programming language. NLP is typically enabled via machine learning, but Kore.ai uses a multi-engine approach which includes intent recognition and entity extraction.
NLP enables an IVA to identify the user intents; extract useful information from their utterances and map the data (entities) to the relevant tasks. The Kore.ai XO Platform’s NLP strategy includes combining Fundamental Meaning, Machine Learning, and Knowledge Graph Engines for optimal conversational accuracy. IVAs built on the XO Platform can understand and process:
- Multi-sentence messages
- Multiple intents
- Contextual references
- Patterns and idiomatic sentences, and more.
Natural Language Training
The processes by which you refine an intelligent virtual assistant’s ability to understand and process natural language requests, and test accordingly. It can be done by adding synonyms to the IVA’s vocabulary via the Bot Builder, or by training it with complete utterances via machine learning. You can learn more about how to train a bot by watching How To Build an IVA In 5 Minutes.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
Natural Language Understanding is part of Natural Language Processing and refers to the IVAs ability to process user utterances, identify their meaning, and integrate them with existing training data.
Neural networks
A computer system modeled on the human brain and nervous system.
Node
A node is where different points of a dialog or workflow intersect. The Dialog Builder has multiple node types so developers can guide the human-to-bot conversation in different directions using intent nodes, service nodes, message nodes, confirmation nodes, webhook nodes, and JavaScript nodes. Learn more about how you can use nodes to build more complex and free-flowing IVA dialogs.
Omni-Channel (deployment)
The process of building one IVA that is “channel agnostic” (meaning the bot can be implemented in any channel), and deploying it to the communication channels of your choice. Omni-channel bots can be accessed in more than one place and can carry conversation context across channels.
Patterns
Patterns are word combinations that indicate a certain intent or entity.
Pause and Resume
An approach for situations when an IVA receives a task request while in the process of completing an initial request. The bot can then pause one request, complete the more immediate task, and circle back to resume the request it previously put on hold.
Platform Architecture
A visual descriptor of the various Platform features and how they interact with one another.
Pilot
The stage after proof-of-concept where an IVA’s tasks are published and the bot is deployed to a select group of users for testing.
Proof-of-Concept (POC) – The stage where IVA use cases are determined and tasks are built to prove the viability of initial use cases.
Public Bots Store
A bot store that an enterprise sets up with custom bots that can be made available for public users, as opposed to an enterprise bot store which only makes bots available to a select group of enterprise users.
Response Formatting
The process by which a developer customizes the responses a bot will give during an interaction. Responses can be formatted to be natural language only, or include GUI elements such as buttons, forms, images, etc.
Robotic Processing Automation (RPA)
A tool for automating manual, time-consuming, complex, rule-based workflows and functions for back-end IT administrative work.
Sentiment Analysis
Beyond completing tasks, IVAs built on the Kore.ai XO Platform can understand a user’s mood throughout a conversation. Our NLP engine scores sentiment based on connotation, word placement, and modifiers. Developers can use these scores to trigger custom flows to improve bot-to-user communication or bring in human agents as needed.
Service Call
Service calls are used to make API requests to third-party web services to push, pull, or manipulate data. The web service unpacks the request and converts it to a command that the application or system can understand in order to complete the task or return the needed data. The platform then receives that message and unpacks it in order to obtain the results of the request. The XO Platform supports the use of API services to make REST, SOAP, or ODATA requests.
Session
The period of time from when a user engages a bot until they disengage.
Session context
Information specified by a user that is the primary context for a bot to keep in mind during a session.
Software Development Kit (also see Mobile SDK, Web SDK)
Tools or resources that help developers create websites and apps and customize elements of the UI.
Storyboard
A primary feature within the Kore.ai XO Platform that allows developers to visualize and manage the IVA design process through FAQs, Dialog Tasks, and Mock Conversation Scenes.
Structured Data
Information with a high degree of organization that is easily searchable when placed in a database.
Supervised Learning for Natural Language (NL)
Through the Bot Builder tool, developers and admins can support supervised learning and evaluate all interaction logs, easily change NL settings for failed scenarios, and use the learnings to retrain the bot for better conversations. Developers can also leverage chat logs to build predictive models and use the outcomes to further define additional proactive alerts, suggested actions, or automated workflows.
Developers have input variables (X) and an output variable (Y) and use an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to the output Y=f(X). Here, the IVA developer acts as a teacher and has virtually full control over what the IVA learns. This means that the algorithm makes predictions based on the training data provided. The IVA creator or developer can manually correct these predictions by flagging the findings as correct or incorrect. Since the IVA builder already knows what the IVA should understand, learning can be stopped as soon as the developer decides or when the model reaches an acceptable level of performance and maturity.
Tasks
The different types of simple and complex “jobs” a developer designates the IVA to perform. An intelligent virtual assistant can perform 5 types of tasks: alerts, actions, information, knowledge, and dialog tasks.
For example, for an intelligent virtual travel agent, task names are to book tickets, find hotels, provide weather forecasts, etc. that cater to different user intents. Once the IVA understands the intent, it is ready to perform a task, such as reaching out to a web service, extracting the current weather conditions report, parsing that response, and then delivering the data to the user.
Testing
The step-by-step processes of testing request chaining, intent and sub-intent recognition, entity extraction, conversation flows, and more.
Training Data
The amount of data, usually in the form of utterances, that is fed to a bot in order to train it for the purpose of identifying intents and entities, so that the IVA may complete the tasks required by users.
Use Case
The various ways IVAs can be applied for employee and customer-facing tasks. Check out our Top 30 defined use cases for chatbots.
User Context
Individual user information or preferences that can be shared by all enterprise bots the user will interact with, for example, a home address, payment information, etc.
User Experience (UX)
The overall experience of a person using a product, like a website or mobile application. It’s usually gauged by how easy or enjoyable something is to use.
User Interface (UI)
The means by which the user and a computer system interact.
Universal Bot
A bot that has the power to communicate with other bots to complete tasks on its behalf.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data and documents, in this instance, refer to sources that are typically text-heavy and free-flowing. Such documents or data can still contain dates, numbers, and facts, but they lack a pre-defined data model or structure and overall consistency. The XO Platform supports semantic search against unstructured data and the training of bots from unstructured documents.
Unsupervised learning for Natural Learning (NL)
Unsupervised learning for NL can be applied to expand the language capabilities of your VA, without human intervention. Unlike unsupervised models in which IVAs learn from any input, good or bad, the Kore.ai XO Platform enables IVAs to automatically increase their vocabulary only when the IVA successfully recognizes the intent and extracts the entities of a human’s request to complete a task.
Utterance
Anything that a user says to the IVA is an utterance. For example, if the user types “Book me a flight to Orlando for next Sunday”, the entire sentence is considered as the user’s utterance.
Value Added Reseller (VAR)
A value-added reseller offers third-party software and hardware to the end user at a markup, along with some combination of procurement consulting, configuration, and customization services. They generate revenues through a combination of flat-rate fees per license, and billable hours, but their engagement is finite.
Variables, Context, and Session Data
When developers create and define tasks, they can access the following:
- Session variables provided by the XO Platform.
- Custom variables that they define.
- The context that defines the scope of the variable.
For example, some API requests require you to set session variables before executing the task, or a dialog task component needs to access a session variable to transit to the next node. Dialog tasks can also access the context object with additional system variables. These session and context variables allow you to persist and store data.
For example, a user’s home address for e-commerce, transportation, and home delivery-focused services is used by the IVA when executing a task. The XO Platform supports session variables that are used when defining tasks in sections using JavaScript. Session variables depend on the context or scope in which they are used. For example, enterprise-level, IVA-level, user-level, and session-level.
Web SDK
A software development kit that allows developers to customize websites, also a supported channel for bots.
Winning Intent
When the IVA receives a user utterance, it will attempt to detect potential intents, and then score them by the probability that they represent what the user wants. The intent that scores the highest is the one that the IVA responds to and is called a Winning Intent.
Want to Learn More?
We're here to support your learning journey. Ready to take on bot building but not sure where to start? Learn conversational AI skills and get certified on the Kore.ai Experience Optimization (XO) Platform.
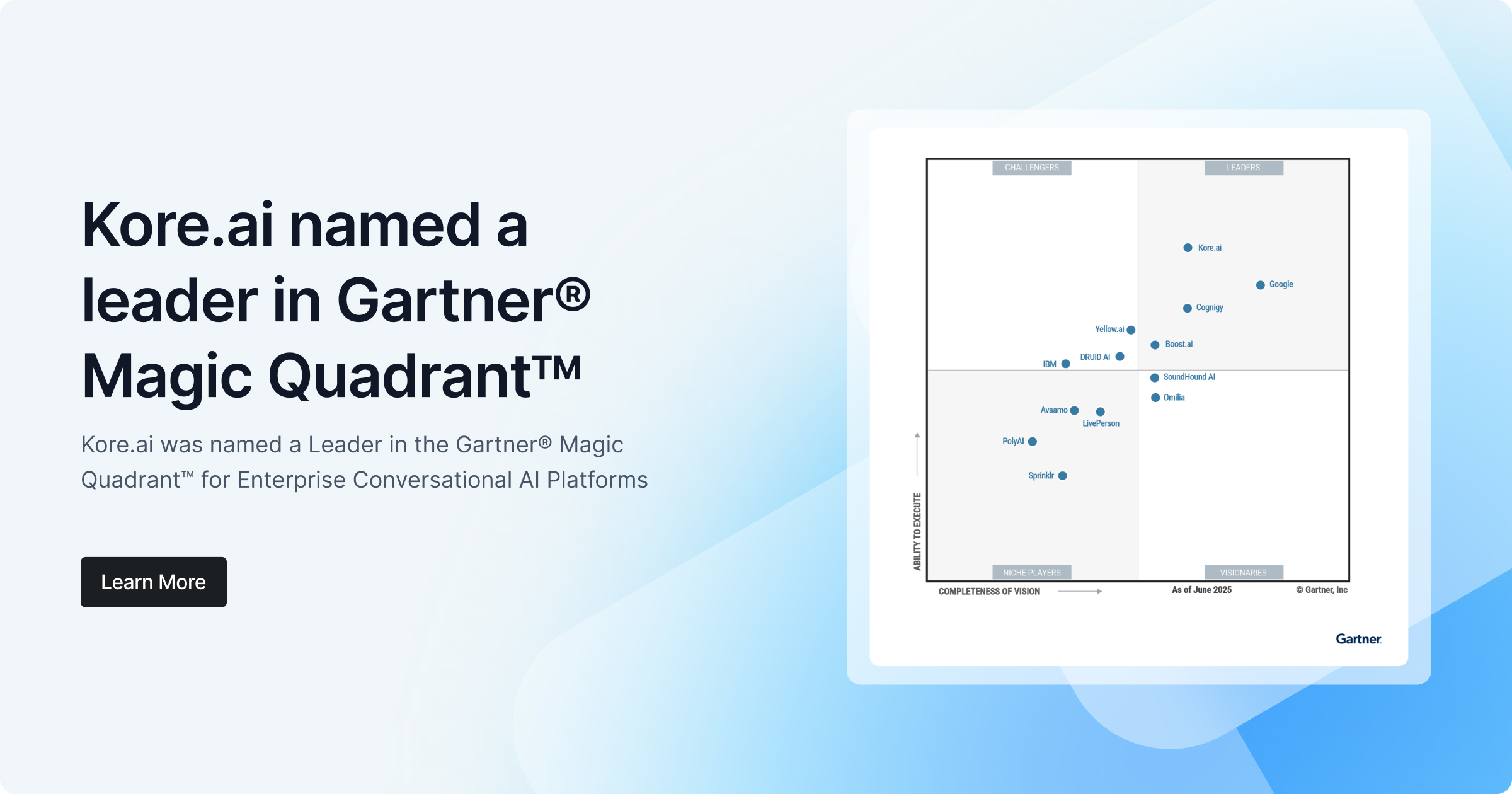
As a leader in conversational AI platforms and solutions, Kore.ai helps enterprises automate front and back-office business interactions to deliver extraordinary experiences for their customers, agents, and employees.





-1.jpg)




